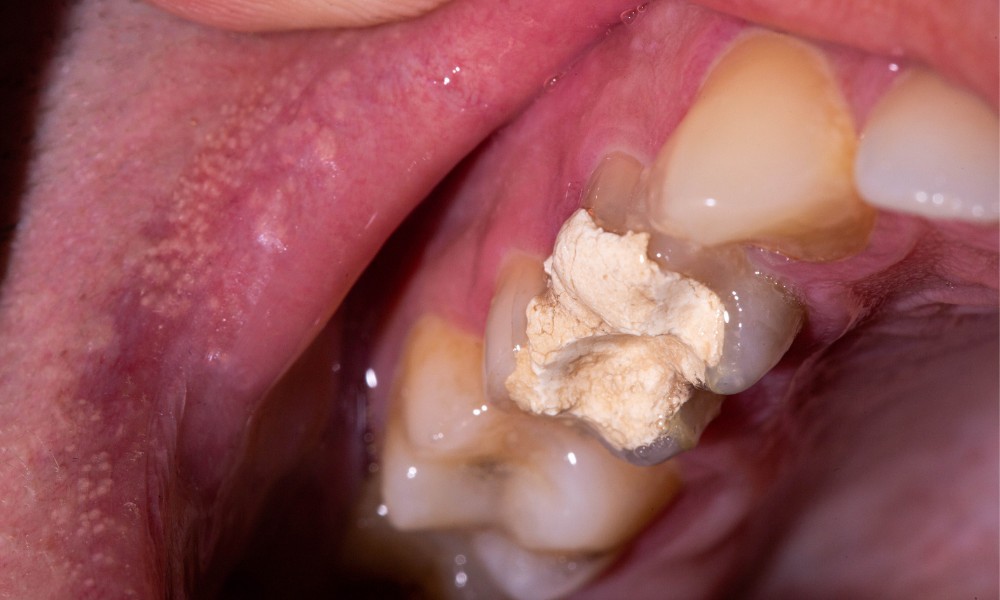
Pulpitis is a painful dental condition characterized by the inflammation of the dental pulp, which is the soft tissue inside the tooth containing blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. This condition can be caused by various factors, including tooth decay, trauma, or gum disease, and can lead to severe pain, sensitivity, and potentially, tooth loss. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent further complications. Treatment options offered by the dentist in Mequon, WI, and their expert team can effectively alleviate painful symptoms and enhance overall health and wellness.
What are the types of pulpitis?
There are two main types of pulpitis:
- Reversible pulpitis: Mild inflammation that can be treated with restorative procedures, such as fillings.
- Irreversible pulpitis: Severe inflammation that requires root canal therapy or tooth extraction.
What causes pulpitis?
Here is a comprehensive list of causes of pulpitis:
- Tooth Decay: Bacterial infection that reaches the pulp
- Trauma: Physical injury to the tooth
- Gum Disease: Infection of the gums that spreads to the pulp
- Cracks or Fractures: Tooth damage that exposes the pulp
- Dental Procedures: Complications from fillings, crowns, or other dental work
- Grinding or Clenching: Repeated stress on the teeth
- Tooth Erosion: Acid wear that exposes the pulp
- Tooth Resorption: Internal or external resorption that exposes the pulp
- Pulpal Calcification: Hardening of the pulp tissue
- Dental Materials: Allergic reactions or toxicity from dental materials
- Bacterial Invasion: Bacteria entering the pulp through various means
- Viral or Fungal Infections: Infections that affect the pulp
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations that affect the pulp
- Aging: Natural aging process that affects the pulp
- Genetic Predisposition: Inherited traits that increase pulpitis risk
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Infrequent brushing, flossing, or dental check-ups
- Diet: Consuming sugary, acidic, or hard foods and drinks
- Smoking: Reduced blood flow and increased risk of pulpitis
- Systemic Diseases: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or autoimmune disorders, that increase pulpitis risk.
What are the symptoms of pulpitis?
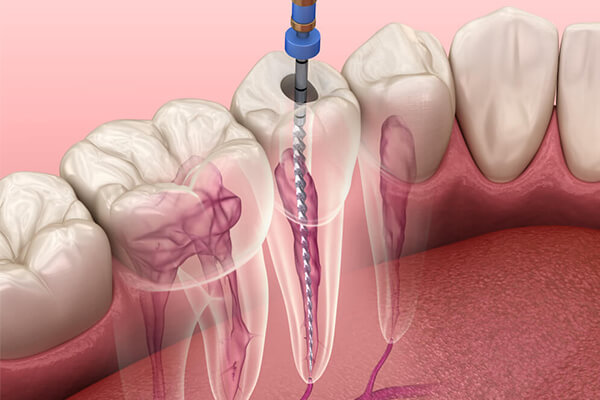
Here is a comprehensive list of pulpitis symptoms:
Common Symptoms:
- Severe pain or discomfort in the affected tooth
- Pain or discomfort when consuming hot or cold foods and drinks
- Inflammation of the surrounding gum tissue
- Darkening of the tooth
- Pain when applying pressure to the tooth
- Pain or discomfort when touching the surrounding gum tissue
- Unpleasant taste or smell from the affected tooth
- Visible pus or discharge from the affected tooth
Less Common Symptoms:
- Elevated body temperature
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck or jaw
- Feeling tired or exhausted
- Pain or discomfort in the head or face
- Pain or discomfort in the ear
- Pain or discomfort when consuming sweet or sour foods and drinks
- Pain when gently tapping the affected tooth
- Bleeding from the surrounding gum tissue
Severe Symptoms:
- Excruciating pain that persists or worsens over time
- Significant swelling that affects facial appearance
- Pain or discomfort when swallowing
- Fever over 101.5°F (38.6°C)
- Visible pus or discharge that does not resolve with treatment
How is pulpitis treated?
Here are some common treatment options:
Reversible Pulpitis:
- Removal of the cause: Remove the source of irritation, such as a cavity or crack.
- Restorative procedures: Fillings, crowns, or other restorations to protect the tooth.
- Pain management: Medication to manage pain and discomfort.
- Monitoring: Regular check-ups to ensure the pulpitis has resolved.
Irreversible Pulpitis:
- Root canal therapy: Remove the infected pulp tissue and clean the canal.
- Pulpectomy: Remove the entire pulp tissue.
- Tooth extraction: Remove the tooth if it’s deemed nonrestorable.
- Pain management: Medication to manage pain and discomfort.
- Antibiotics: To treat any associated infection.
Pulpitis is a painful dental condition that requires prompt attention to prevent further complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take steps to prevent pulpitis and maintain good oral health. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices are essential in preventing pulpitis and ensuring a healthy, pain-free smile.